Content Table
- Introduction
- Importance of Workplace Culture
- Quote from Herb Kelleher
- Why Culture Matters
- Definition of Culture
- Alignment Between Strategy and Behavior
- Understanding Emotional Culture
- Distinction Between Cognitive and Emotional Culture
- Examples of Unmanaged Emotional Culture
- Impact of Emotional Culture During Organizational Change
- The Science of Emotions
- Role of Emotions in Workplace Interactions
- Influence of Positive Emotions
- Influence of Negative Emotions
- Research Findings on Emotions in High-Performing Organizations
- How to Measure Emotional Culture
- Challenges with Traditional Engagement Surveys
- Innovative Approaches to Measuring Emotional Culture
- Introduction to Emotional Culture Surveys
- The Emotional Culture Index (ECI)
- Overview of ECI Dimensions:
- Current State
- Expected State
- Ideal State
- Benefits of Measuring Emotional Culture with ECI
- Customization Options for the Survey
- Overview of ECI Dimensions:
- Why Emotional Culture Matters for Organizations
- Bridging the Emotional Gap
- Linking Emotional Culture to Learning and Development
- Striving to Be a Great Place to Work
- Summary
A lot of different elements underlie organizational success. You’ve got to be in the right place, at the right time, with the right product and with the right people. But even with the best of these, a great workplace culture truly matters. Do you know the emotional culture of your organization?
Eventually competitors can come along and replicate your best practices, strategies and processes. As Herb Kelleher from Southwest Airlines once famously said “All airlines have aeroplanes.”
According to Kelleher, “We’ve never had layoffs. We could have made more money if we furloughed people. But we don’t do that. And we honor them constantly. Our people know that if they are sick, we will take care of them. If there are occasions of grief or joy, we will be there with them. They know that we value them as people, not just cogs in a machine.”
So consequently, culture matters.
Culture is defined many ways, one of the more commercial ways of thinking about it is this, culture is the degree of alignment between strategy and the way employees think and behave.
In 2016, HBR ran an article titled Manage Your Emotional Culture. The article talks about and distinguishes between Cognitive Culture and Emotional Culture. It goes on to talk about the fact that emotional culture is rarely managed as deliberately as cognitive culture and that it’s often not managed at all. It gives some great examples of how much companies suffer as a result. Employees who should be showing compassion (in health care, for example become callous and indifferent. Teams that would benefit from joy and pride instead tolerate a culture of anger. People who lack a healthy amount of fear (say, in security firms or investment banks) act recklessly. The effects can be especially damaging during times of upheaval, such as organisational restructurings and financial downturns.
WHERE TO START IN UNDERSTANDING EMOTIONAL CULTURE?
To discuss and understand the concept of emotional intelligence and emotional culture, first we need to look at the underlying science of emotions. Why do we react the way we do, how does others’ behaviour impact us the way it does?
We all experience a wide range of pleasant and unpleasant feelings at work as we interact with colleagues, customers, suppliers and others. These feelings influence our decisions, behaviour and performance.
Pleasant feelings have a ‘broaden and build’ effect causing us to think more broadly, engage more deeply and perform better.

Unpleasant emotions tend to have a ‘narrowing and limiting’ effect, causing us to be more closed-minded, less engaging and poorer at performing. Collectively, these emotions impact the bottom-line for better or worse.
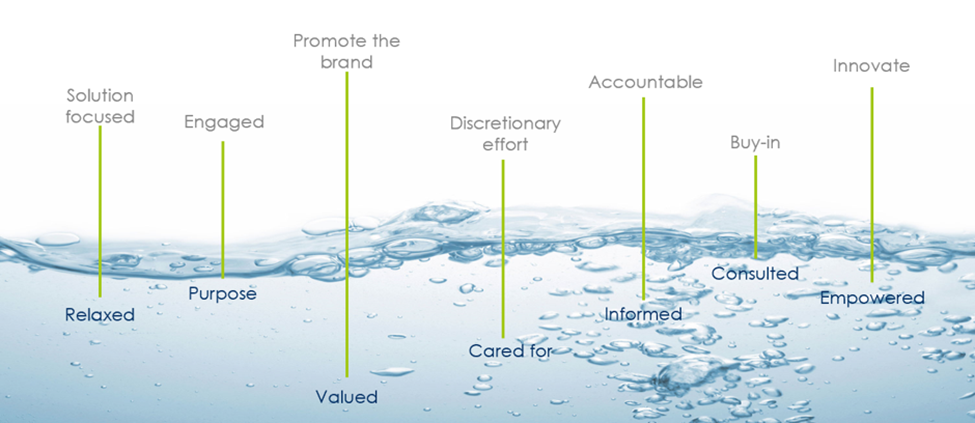
Let’s start with positive/pleasant emotions. Think about your experiences in the workplace for a moment. When people feel relaxed at work, they tend to be solution focused. When they feel involved, they often promote the brand. When they feel cared for by the company, they go above and beyond in the level of discretionary effort they put towards the company. Finally, employees that are empowered are often the hardest working and innovative team members.
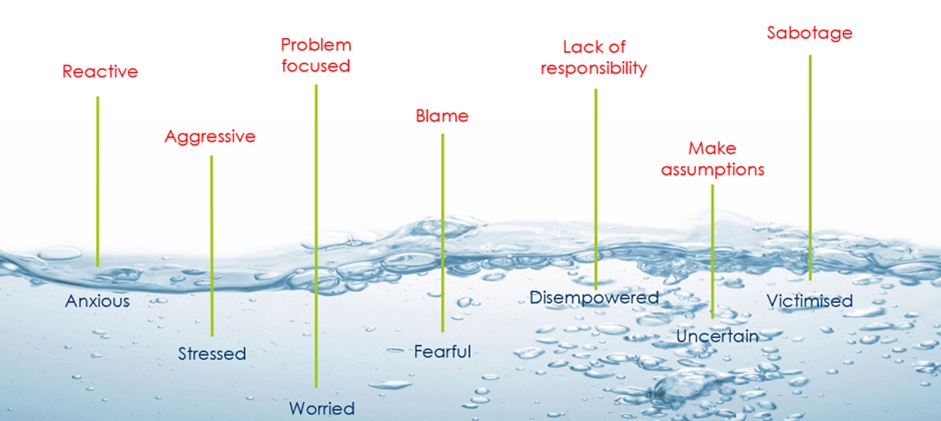
Conversely, let’s look at negative or unpleasant emotions. When people feel anxious, they are more likely to be reactive. When stressed, we can become aggressive. It’s human nature. When an employee feels fearful, they can sometimes blame others. Finally, when people feel disempowered, they can assume a lack of responsibility and ownership for their work. We’ve all been there.
Research shows that people in high performing organisations experience more positive emotions and fewer negative emotions than those in low performing organisations. (Boedker et al. 2011)
So why aren’t more organisations working to focus on understanding how their people are feeling and managing their EMOTIONAL CULTURE?
DO YOU KNOW HOW YOUR PEOPLE ARE FEELING RIGHT NOW?
Often, companies release employee engagement surveys that are confidential, but staff that are struggling or feeling fearful may not respond in the most honest way for fear of repercussion. Or some measure Net Promoter Score – how likely you are to recommend a company to others or as a customer, how likely you are to recommend the products. Some organisations have even had volunteers use wearables to measure things like tone of voice, body language, frequency of social interactions, and participation in meetings.
Emotional culture surveys are the most direct and impactful way to measure emotional culture because they measure three distinct things to help identify whether or not emotions experienced need to shift. They measure:
- Experienced emotions
- Expected emotions
- Ideal or desirable levels of emotions
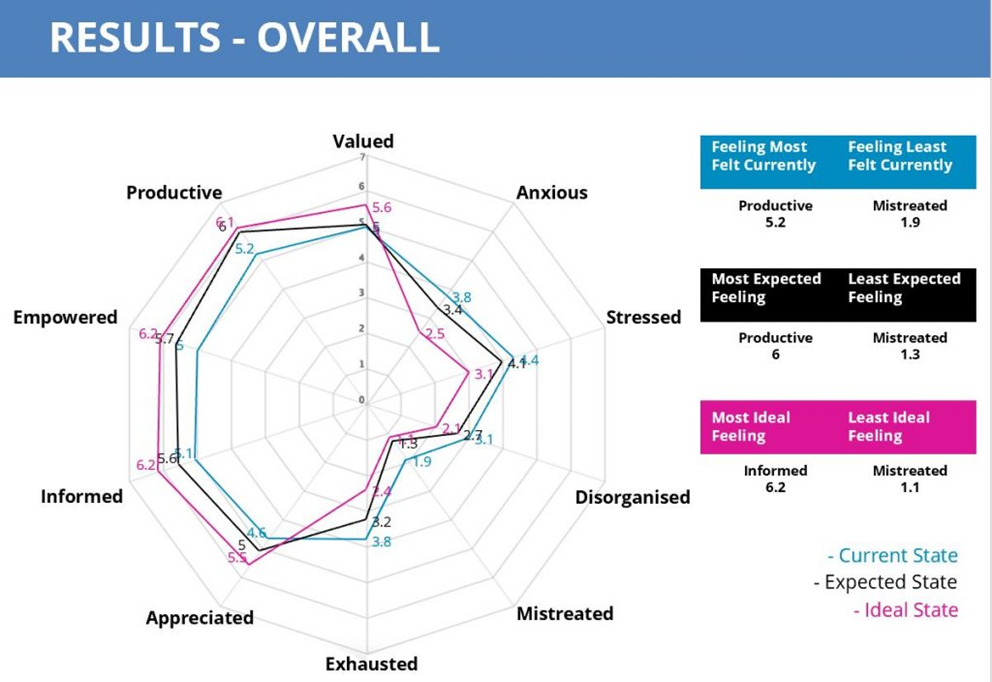
When you understand how your people are feeling, how they’d ideally like to feel and where the gaps are – you can do something about it. It allows you to more easily understand where the differences are – so you can be informed in making decisions for your L&D, training and development of your teams and workplace culture. You can continue to strive to be a great place to work.
We’d like to give you the opportunity to do so by experiencing The Emotional Culture Index from Genos International.
The Emotional Culture Index is designed to measure three dimensions of emotions at work:
- Current state – How often your people experience certain feelings at work.
- Expected state – How often your people think its fair and reasonable to experience these feelings at work given the nature and context of your workplace.
- Ideal state – How often your people think they should ideally experience these feelings in your workplace in order to be effective.
It also allows participants to share confidential free text responses on key areas. You can customise the survey by department, team, region or a particular demographic or group.
It takes only a few minutes to complete, and you will receive a report with its findings and have the opportunity to discuss privately with a me, a Genos Certified Emotional Intelligence Practitioner.
As we enter into a world of AI, automation and machine led learning, our ability to feel and be human is what makes us unique. We encourage you to take this limited time opportunity to uncover your emotional culture.
SUMMARY
Summary of the Blog
Workplace culture is key to organizational success, with emotional culture often overlooked compared to cognitive culture. Positive emotions like feeling valued and empowered boost engagement, innovation, and performance, while negative emotions like stress and fear lead to disengagement and reduced productivity.
The Emotional Culture Index (ECI) helps organizations measure current, expected, and ideal emotional states, providing actionable insights to align workplace culture with employee needs. By addressing emotional gaps, businesses can foster a thriving, emotionally intelligent environment that enhances team dynamics and long-term success.
Take the first step toward understanding your organization’s emotional culture with the ECI.





